File Formats
Learning Objective
Upon completion of this section you will have a better understanding of the following file formats, how to read them and interpret the information they contain.
- FASTA – plain sequences
- FASTQ – sequencing reads
- GFF – gene models
- GTF - variation of GFF
- VCF – sequence variants
- SAM – sequence alignments
- BAM – alignments in binary
FASTA
Text file format for storing sequences for nucleotide & amino acid data. For a given sequence, a single line description and ID is supplied followed by one or more lines of sequence. Multiple sequences can be placed in a single file and empty lines are typically ignored by programs. The recommended number of sequence characters per line is 60 – 80.
1
2
Line 1: starts with “>” followed by ID
Line 2: Sequence data
Examples for FASTA file
1
2
3
>gi|296581|emb|Z22600.1| D.tigrina homeodomain mRNA
ttcgcggttcataactacctgacgaggttgagacggtacgagctggcggtggccctcaatcttaacgaaa
gacagataaaagtttgg
1
2
3
>gi|425153|gb|L26238.1|MUSHOME Mus domesticus (lbx) homeodomain mRNA, partial cds
CCATTTCAACAAGTACCTGACCAGGGCTCGGCGAGTGGAAGTTGCCGCTATTCTCGAGCTCAACGAAACT
CAAGTGAAAATT
1
2
3
4
5
>gi|2695691|gb|AAC36493.1| BRCA1 [Rattus norvegicus]
MDLSAVRIQEVQNVLHAMQKILECPICLELIKEPVSTQCDHIFCKFCMLKLLNQKKGPSQCPLCKNEITK
RSLQGSARFSQLVEELLKIIDAFELDTGMQCANGFSFSKKKNSSSELLNEDASIIQSVGYRNRVKKLQQI
ESGSATLKDSLSVQLSNLGIVRSMKKNRQTQPQNKSVYIALESDSSEERVNAPDGCSVRDQELFQIAPGG
AGDEGKLNSAKKAACDFSEGIRNIEHHQCSDKDLNPTENHATERHPEKCPRISVANVHVEPCGTDARASS
Common Errors that occur with FASTA file
- Program requires the sequences to be all on a single line but the FASTA file is on multiple lines
- Program requires the sequences to be on multiple lines with a string length per line less than 80 characters but the sequences are written on a single line
FASTQ
FASTQ files are similar to FASTA but also contain the quality score of the sequence data (only nucleotide sequences). The format contains two additional lines beyond FASTA format.
1
2
3
4
Line 1: starts with “@” followed by ID
Line 2: Sequence data
Line 3: Starts with “+” rest of the description is optional
Line 4:Quality score for each base in the sequence
Example for FASTQ file
1
2
3
4
@HISEQ:402:H147CADXX:1:1101:1250:2208 1:N:0:CGATGT
TGATGCTGCNAATTTTATTCAGTCAGCGGAGGGGGCTTACGTGTATTTTCTGCAACCTTT
+
CCCFFFFFH#4AFIJJJJJJJJIJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJHHHHHHFFFFFFFEEEEED
Quality score
- Probability of an error in base calling
- Higher score means lower probability of error
- Quality scores are often represented as ASCII characters
- Here are the ASCII characters in left-to-right increasing order of quality:
1
!"#$%&'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~
- The rule for converting an ASCII character to an integer varies
- Different types of encoding available (Sanger, Phred, etc..)
- Different sequencing technologies use different encoding
For more information on Quality Score encoding see Fastq Quality score Encoding
GFF: General Feature Format
This is a nine column tab separated text file that stores information about gene annotation. It has several versions which are similar but not compatible
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Column 1 seqID (e.g. chromosome/scaffold, genome id, etc..)
Column 2 Source (program used to generate or location of download)
Column 3 Feature type (gene, mRNA, CDS, exon, etc.)
Column 4 Start position of feature
Column 5 End position of feature
Column 6 Score (some program outputs will have a score of confidence for feature)
Column 7 Strand (+,-,.)
Column 8 Phase
Column 9 List of attributes in the format tag=value. Multiple attributes are separated by “;”
Undefined fields are replaced with “.” character
In GFF3 format, the first line ## gff -version 3 is mandatory.
Examples for GFF file
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
##gff-version 3
##date Thu Nov 7 15:29:10 2013
##source gbrowse gbgff gff3 dumper
Chr1 TAIR9 gene 813471 816749 . + . ID=AT1G03310;Note=protein_coding_gene;Name=AT1G03310
Chr1 TAIR9 mRNA 813471 816749 . + . ID=AT1G03310.1;Parent=AT1G03310;Name=AT1G03310.1;Index=1
Chr1 TAIR9 protein 813975 816623 . + . ID=AT1G03310.1-Protein;Name=AT1G03310.1;Derives_from=AT1G03310.1
Chr1 TAIR9 exon 813471 813581 . + . Parent=AT1G03310.1
Chr1 TAIR9 five_prime_UTR 813471 813581 . + . Parent=AT1G03310.1
Chr1 TAIR9 exon 813929 816749 . + . Parent=AT1G03310.1
Chr1 TAIR9 five_prime_UTR 813929 813974 . + . Parent=AT1G03310.1
Chr1 TAIR9 CDS 813975 816623 . + 0 Parent=AT1G03310.1,AT1G03310.1-Protein;
Chr1 TAIR9 three_prime_UTR 816624 816749 . + . Parent=AT1G03310.1
Chr1 TAIR9 mRNA 813486 816749 . + . ID=AT1G03310.2;Parent=AT1G03310;Name=AT1G03310.2;Index=1
Chr1 TAIR9 protein 813975 816623 . + . ID=AT1G03310.2-Protein;Name=AT1G03310.2;Derives_from=AT1G03310.2
Chr1 TAIR9 exon 813486 813604 . + . Parent=AT1G03310.2
Chr1 TAIR9 five_prime_UTR 813486 813604 . + . Parent=AT1G03310.2
Chr1 TAIR9 exon 813929 816749 . + . Parent=AT1G03310.2
Chr1 TAIR9 five_prime_UTR 813929 813974 . + . Parent=AT1G03310.2
Chr1 TAIR9 CDS 813975 816623 . + 0 Parent=AT1G03310.2,AT1G03310.2-Protein;
Chr1 TAIR9 three_prime_UTR 816624 816749 . + . Parent=AT1G03310.2
Chr1 TAIR9 gene 795532 798463 . - . ID=AT1G03260;Note=protein_coding_gene;Name=AT1G03260
Chr1 TAIR9 mRNA 795532 798463 . - . ID=AT1G03260.1;Parent=AT1G03260;Name=AT1G03260.1;Index=1
Chr1 TAIR9 protein 795678 798102 . - . ID=AT1G03260.1-Protein;Name=AT1G03260.1;Derives_from=AT1G03260.1
Chr1 TAIR9 five_prime_UTR 798103 798463 . - . Parent=AT1G03260.1
Chr1 TAIR9 CDS 798001 798102 . - 0 Parent=AT1G03260.1,AT1G03260.1-Protein;
Chr1 TAIR9 exon 798001 798463 . - . Parent=AT1G03260.1
Chr1 TAIR9 gene 799191 802436 . + . ID=AT1G03270;Note=protein_coding_gene;Name=AT1G03270
Chr1 TAIR9 mRNA 799191 802436 . + . ID=AT1G03270.1;Parent=AT1G03270;Name=AT1G03270.1;Index=1
Chr1 TAIR9 protein 799191 802436 . + . ID=AT1G03270.1-Protein;Name=AT1G03270.1;Derives_from=AT1G03270.1
Chr1 TAIR9 exon 799191 799431 . + . Parent=AT1G03270.1
Following example is the canonical gene definition by Lincoln Stein
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
##gff-version 3
##sequence-region ctg123 1 1497228
ctg123 . gene 1000 9000 . + . ID=gene00001;Name=EDEN
ctg123 . TF_binding_site 1000 1012 . + . ID=tfbs00001;Parent=gene00001
ctg123 . mRNA 1050 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00001;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.1
ctg123 . mRNA 1050 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00002;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.2
ctg123 . mRNA 1300 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00003;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.3
ctg123 . exon 1300 1500 . + . ID=exon00001;Parent=mRNA00003
ctg123 . exon 1050 1500 . + . ID=exon00002;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00002
ctg123 . exon 3000 3902 . + . ID=exon00003;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00003
ctg123 . exon 5000 5500 . + . ID=exon00004;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00002,mRNA00003
ctg123 . exon 7000 9000 . + . ID=exon00005;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00002,mRNA00003
##gff-version 3
##sequence-region ctg123 1 1497228
ctg123 . gene 1000 9000 . + . ID=gene00001;Name=EDEN
ctg123 . TF_binding_site 1000 1012 . + . ID=tfbs00001;Parent=gene00001
ctg123 . mRNA 1050 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00001;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.1
ctg123 . mRNA 1050 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00002;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.2
ctg123 . mRNA 1300 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00003;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.3
ctg123 . exon 1300 1500 . + . ID=exon00001;Parent=mRNA00003
ctg123 . exon 1050 1500 . + . ID=exon00002;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00002
ctg123 . exon 3000 3902 . + . ID=exon00003;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00003
ctg123 . exon 5000 5500 . + . ID=exon00004;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00002,mRNA00003
ctg123 . exon 7000 9000 . + . ID=exon00005;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00002,mRNA00003
ctg123 . CDS 1201 1500 . + 0 ID=cds00001;Parent=mRNA00001;Name=edenprotein.1
ctg123 . CDS 3000 3902 . + 0 ID=cds00001;Parent=mRNA00001;Name=edenprotein.1
ctg123 . CDS 5000 5500 . + 0 ID=cds00001;Parent=mRNA00001;Name=edenprotein.1
ctg123 . CDS 7000 7600 . + 0 ID=cds00001;Parent=mRNA00001;Name=edenprotein.1
ctg123 . CDS 1201 1500 . + 0 ID=cds00002;Parent=mRNA00002;Name=edenprotein.2
ctg123 . CDS 5000 5500 . + 0 ID=cds00002;Parent=mRNA00002;Name=edenprotein.2
ctg123 . CDS 7000 7600 . + 0 ID=cds00002;Parent=mRNA00002;Name=edenprotein.2
ctg123 . CDS 3301 3902 . + 0 ID=cds00003;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.3
ctg123 . CDS 5000 5500 . + 1 ID=cds00003;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.3
ctg123 . CDS 7000 7600 . + 1 ID=cds00003;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.3
ctg123 . CDS 3391 3902 . + 0 ID=cds00004;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.4
ctg123 . CDS 5000 5500 . + 1 ID=cds00004;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.4
ctg123 . CDS 7000 7600 . + 1 ID=cds00004;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.4
More information on GFF3 files
GTF: Gene Transfer Formats
GTF is a slight variation on GFF. The first 8 columns are the same. The 9th column has a different syntax requiring two attributes
- gene_id
- transcript_id
Each attribute consist of a type/value pare which should be separated with exactly one space and should end in “;”
Example for GTF file
1
2
3
4
5
AB000381 Twinscan CDS 380 401 . + 0 gene_id "001"; transcript_id "001.1";
AB000381 Twinscan CDS 501 650 . + 2 gene_id "001"; transcript_id "001.1";
AB000381 Twinscan CDS 700 707 . + 2 gene_id "001"; transcript_id "001.1";
AB000381 Twinscan start_codon 380 382 . + 0 gene_id "001"; transcript_id "001.1";
AB000381 Twinscan stop_codon 708 710 . + 0 gene_id "001"; transcript_id "001.1";
GFF for comparison
1
2
3
4
ctg123 . mRNA 1050 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00001;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.1
ctg123 . mRNA 1050 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00002;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.2
ctg123 . mRNA 1300 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00003;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.3
VCF: Variant Call Format
VCF is a text file for storing sequence variants, SNPs and InDels. Unlike other formats VCF does not store all of the redundant genetic data that is shared across the genomes.
- Meta data lines : each line starts with ## followed by key=value pairs
- single header line : starts with single # and describes columns in the data lines
- data lines: sequence variation data
Meta data lines
Should start with a single “fileformat” line
1
##fileformat=format verstion number
it is strongly recommended that meta data includes INFO, FILTER and FORMAT lines.
INFO
First four keys are mandatory
1
##INFO=<ID=GT,Number=number,Type=type,Description="description",Source="source",Version="version">
FILTER
1
##FILTER=<ID=ID,Description="description">
FORMAT
1
##FORMAT=<ID=ID,Number=number,Type=type,Description="description">
Header line
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT sample1 sample2 ... sampleN
Column 1: CHROM – chromosome name
Column 2: POS – position in the chromosome
Column 3: ID – identifier
Column 4: REF – reference base(s) in the reference genome
Column 5: ALT – alternate base(s) in the comparing sequence
Column 6: QUAL – quality score
Column 7: FILTER – filter status
Column 8: INFO – additional information
Column 9: FORMAT – genotype information
Column 10: sample–1
Column 11: sample–2 and so on …
VCF Data line Examples
1
2
3
4
Chr1 27767199 . G GA 743.73 . AC=2;AF=1.00;AN=2;BaseQRankSum=-1.985;ClippingRankSum=-0.117;DP=42;FS=0.000;MLEAC=2;MLEAF=1.00;MQ=41.32;MQ0=0;MQRankSum=-1.129;QD=17.71;ReadPosRankSum=-0.195 GT:AD:DP:GQ:PL 1/1:2,30:32:38:781,38,0
Chr1 27767571 . CATAT C 814.73 . AC=2;AF=1.00;AN=2;DP=46;FS=0.000;MLEAC=2;MLEAF=1.00;MQ=43.25;MQ0=0;QD=4.43 GT:AD:DP:GQ:PL 1/1:0,19:19:64:852,64,0
Chr1 27768362 . T C 1676.77 . AC=2;AF=1.00;AN=2;DP=39;FS=0.000;MLEAC=2;MLEAF=1.00;MQ=39.97;MQ0=0;QD=31.09 GT:AD:DP:GQ:PL 1/1:0,39:39:99:1705,117,0
Chr1 27768651 . A ATG 1909.73 . AC=2;AF=1.00;AN=2;DP=52;FS=0.000;MLEAC=2;MLEAF=1.00;MQ=43.32;MQ0=0;QD=18.36 GT:AD:DP:GQ:PL 1/1:0,44:44:99:1947,129,0
Example for VCF file
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
##fileformat=VCFv4.1
##FILTER=<ID=LowQual,Description="Low quality">
##FORMAT=<ID=AD,Number=.,Type=Integer,Description="Allelic depths for the ref and alt alleles in the order listed">
##FORMAT=<ID=DP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Approximate read depth (reads with MQ=255 or with bad mates are filtered)">
##FORMAT=<ID=GQ,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Genotype Quality">
##FORMAT=<ID=GT,Number=1,Type=String,Description="Genotype">
##INFO=<ID=AC,Number=A,Type=Integer,Description="Allele count in genotypes, for each ALT allele, in the same order as listed">
##INFO=<ID=AF,Number=A,Type=Float,Description="Allele Frequency, for each ALT allele, in the same order as listed">
##INFO=<ID=AN,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Total number of alleles in called genotypes">
##INFO=<ID=BaseQRankSum,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Z-score from Wilcoxon rank sum test of Alt Vs. Ref base qualities">
##INFO=<ID=ClippingRankSum,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Z-score From Wilcoxon rank sum test of Alt vs. Ref number of hard clipped bases">
##INFO=<ID=DP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Approximate read depth; some reads may have been filtered">
##INFO=<ID=DS,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="Were any of the samples downsampled?">
##INFO=<ID=FS,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Phred-scaled p-value using Fisher's exact test to detect strand bias">
##INFO=<ID=HaplotypeScore,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Consistency of the site with at most two segregating haplotypes">
##contig=<ID=Chr4,length=18585056>
##contig=<ID=Chr5,length=26975502>
##contig=<ID=chloroplast,length=154478>
##contig=<ID=mitochondria,length=366924>
##reference=file:///projects/Arabidopsis.fasta
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT Sample1
Chr1 27767199 . G GA 743.73 . AC=2;AF=1.00;AN=2;BaseQRankSum=-1.985;ClippingRankSum=-0.117;DP=42;FS=0.000;MLEAC=2;MLEAF=1.00;MQ=41.32;MQ0=0;MQRankSum=-1.129;QD=17.71;ReadPosRankSum=-0.195 GT:AD:DP:GQ:PL 1/1:2,30:32:38:781,38,0
Chr1 27767571 . CATAT C 814.73 . AC=2;AF=1.00;AN=2;DP=46;FS=0.000;MLEAC=2;MLEAF=1.00;MQ=43.25;MQ0=0;QD=4.43 GT:AD:DP:GQ:PL 1/1:0,19:19:64:852,64,0
Chr1 27768362 . T C 1676.77 . AC=2;AF=1.00;AN=2;DP=39;FS=0.000;MLEAC=2;MLEAF=1.00;MQ=39.97;MQ0=0;QD=31.09 GT:AD:DP:GQ:PL 1/1:0,39:39:99:1705,117,0
Chr1 27768651 . A ATG 1909.73 . AC=2;AF=1.00;AN=2;DP=52;FS=0.000;MLEAC=2;MLEAF=1.00;MQ=43.32;MQ0=0;QD=18.36 GT:AD:DP:GQ:PL 1/1:0,44:44:99:1947,129,0
More information for VCF files
SAM: Sequence Alignment/Map
SAM is a tab limited text file that stores sequence alignments. SAM includes two sections:
- Header section
- Alignment section
Header sections
Header lines start with @ and are optional but if present they should be placed prior to alignment lines.
Each field has a TAG:Value format.
Header record types
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| @HD | The header line |
| @SQ | Reference sequence dictionary |
| @RG | Group read |
| @PG | program |
| @CO | One line comment |
More information on Tags and their values can be found at SAM specifications PDF
Alignment section
Each alignment line has 11 mandatory columns
Mandatory columns in alignment lines
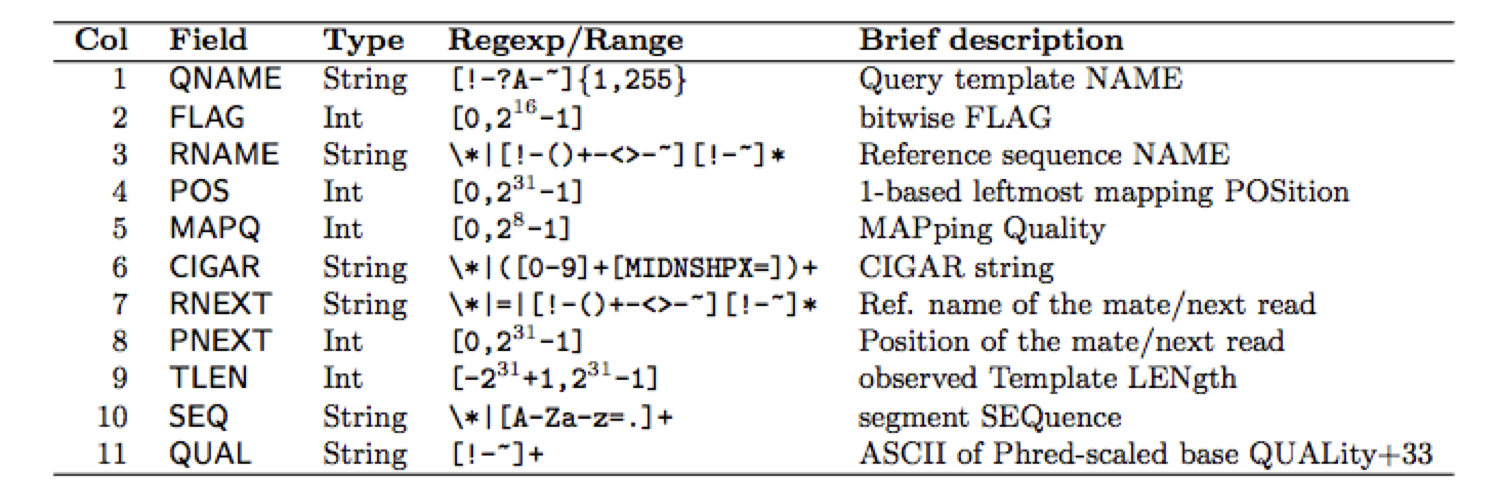
Examples for alignment lines
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
HISEQ:496:C4KY7ACXX:8:1101:1606:2994 73 4 13740599 36 100M * 0 0
ATCACAAAGAATATTCATCAATGCTTCACAAAACATTGGAAGGGGTAATAATGATGGAGACGTTTCCAAAAACAACCGTTGATGTTTTTCCATTGTTTCT
;;?=?;=BDDCA:CEEE@4A?,AEB?A?9A?<+?::?CCCD1))08?BD4B?<BBD:C=)(5-;A7@AA=CC/=??(3>@5;;AD###############
MD:Z:32G10T45G5G4 NH:i:1 HI:i:1 NM:i:4 SM:i:36 XQ:i:40 X2:i:0 XO:Z:HU PG:Z:A
HISEQ:496:C4KY7ACXX:8:1101:1606:2994 133 * 0 0 * 4 13740599 0
ATACAATCGAAAATCATAGTTATTTATGCTCATTCATCGGAAGCTGGGGCAGACTGTTTCAGACAATTACCCATTATTTCTCGAACACTTGAACTAGCAT
(85@34?#############################################################################################
XO:Z:HU
FLAG definition
Flag describes the combination of bitwise FLAGs. Each flag value represent a certain combination of features of the alignment. Every bit is related to the absence (0) or presence (1) of a feature.
Each bit is defined in the following table:
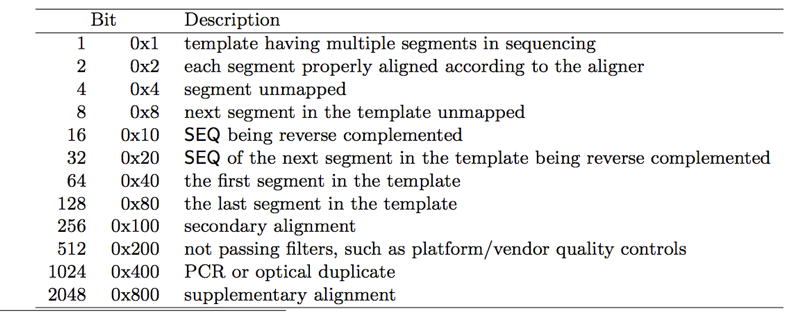
For example Flag value of 17 means that the read is mapped on the reverse strand and it has multiple segments. There are tools to convert the combination value to a feature list such as https://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/explain-flags.html
CIGAR string definition
CIGAR describes how the read aligns with the reference. It consists of one or more components. Each component comprises an operator and the number of bases which the operator applies to. The following table gives an overview of these operators
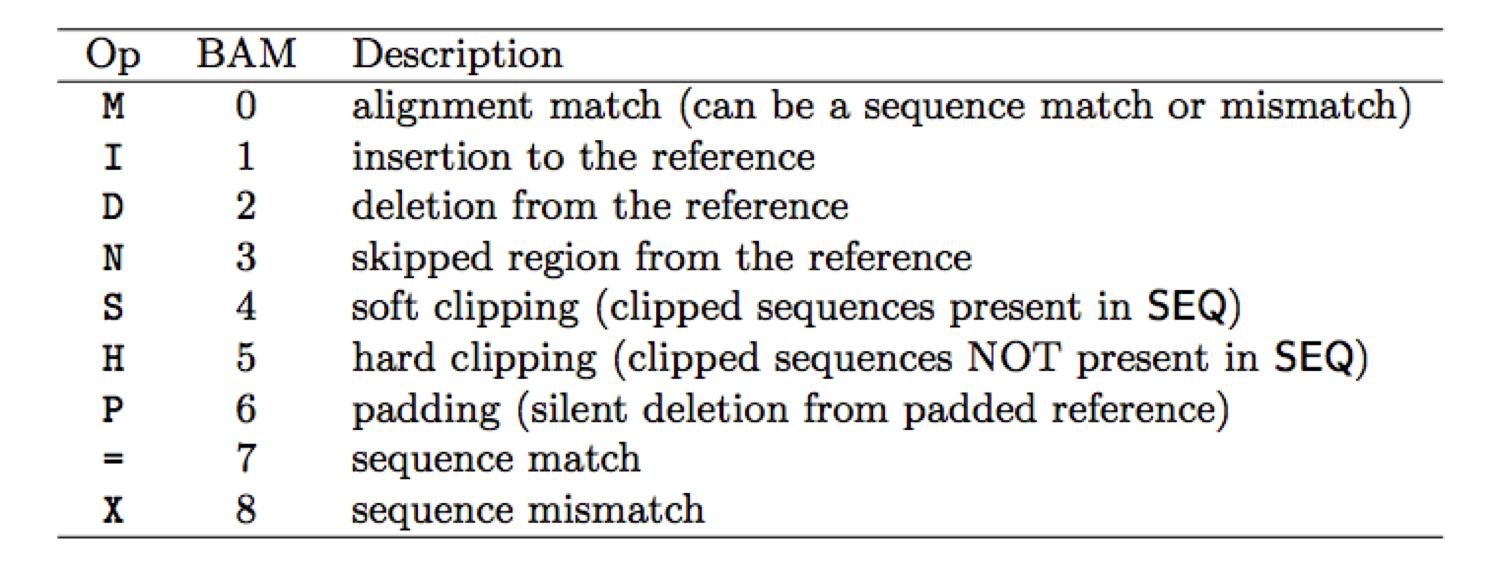
CIGAR Example
for the following alignment:
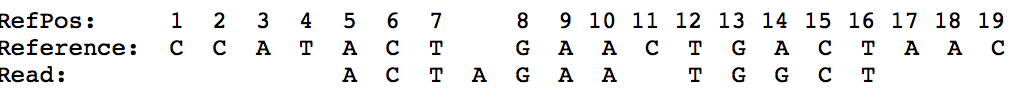
we get:
1
2
POS: 5
CIGAR: 3M1I3M1D5M
The POS indicate that the read aligns start at position 5 on the reference. The first 3 bases in the read align with the reference (3M). The next base is missing on the reference (1I). The next 3 bases align (3M). The next base is missing in the read (1D). Then 5 more bases match with the reference (5M).
More examples for CIGAR
1
2
3
100M – 100 matches
2S98M – 2 soft clipped followed by 98 matches
61M3I36M – 61 matches, 3 insertions, 36 matches
Example for SAM file
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
@HD VN:1.0 SO:unsorted
@PG ID:GSNAP PN:gsnap VN:2014-06-10 CL:gsnap -d TAIR10 --dir=./GSNAPdb//TAIR10 --failed-input=./GSNAPout//1ab-1_failed_alignments -t 4 -N 1 -B 5 -m 5 --part=0/8 --input-buffer-size=1000000 --output-buffer-size=1000000 -A sam --split-output=./GSNAPout//OUT.gsnap.1ab-1_CGATGT_L008_R1_001.fastq.0.8 .//1ab-1_CGATGT_L008_R1_001.fastq .//1ab-1_CGATGT_L008_R2_001.fastq
@SQ SN:1 LN:30427671
@SQ SN:2 LN:19698289
@SQ SN:3 LN:23459830
@SQ SN:4 LN:18585056
@SQ SN:5 LN:26975502
@SQ SN:chloroplast LN:154478
@SQ SN:mitochondria LN:366924
HISEQ:496:C4KY7ACXX:8:1101:1606:2994 73 4 13740599 36 100M * 0 0 ATCACAAAGAATATTCATCAATGCTTCACAAAACATTGGAAGGGGTAATAATGATGGAGACGTTTCCAAAAACAACCGTTGATGTTTTTCCATTGTTTCT ;;?=?;=BDDCA:CEEE@4A?,AEB?A?9A?<+?::?CCCD1))08?BD4B?<BBD:C=)(5-;A7@AA=CC/=??(3>@5;;AD############### MD:Z:32G10T45G5G4 NH:i:1 HI:i:1 NM:i:4 SM:i:36 XQ:i:40 X2:i:0 XO:Z:HU PG:Z:A
HISEQ:496:C4KY7ACXX:8:1101:1606:2994 133 * 0 0 * 4 13740599 0 ATACAATCGAAAATCATAGTTATTTATGCTCATTCATCGGAAGCTGGGGCAGACTGTTTCAGACAATTACCCATTATTTCTCGAACACTTGAACTAGCAT (85@34?############################################################################################# XO:Z:HU
More information
BAM: Binary Alignment Map
BAM is the binary format of a SAM file. It has a smaller storage footprint and needs to be decompressed to be human readable.
